
Every manufacturer is under pressure to deliver top-quality products 100 percent of the time. If not caught in time, a few defects could end up costing an organization thousands or even millions of dollars — along with its reputation among customers. Additionally, factories need to maintain work environments free of safety hazards while maximizing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Accomplishing each of these goals requires clear, comprehensive, and up-to-date standard work instructions. In this article, we’ll explore all things manufacturing standard work: what it entails, associated challenges, and best practices for implementing a standard work strategy in your organization.
Standard work: history, purpose, and examples
Standard work refers to the standardization of best practices across manufacturing processes. The goal of standard work, also called “standardized” work, is to ensure that all tasks are completed correctly and efficiently, leaving little room for error.
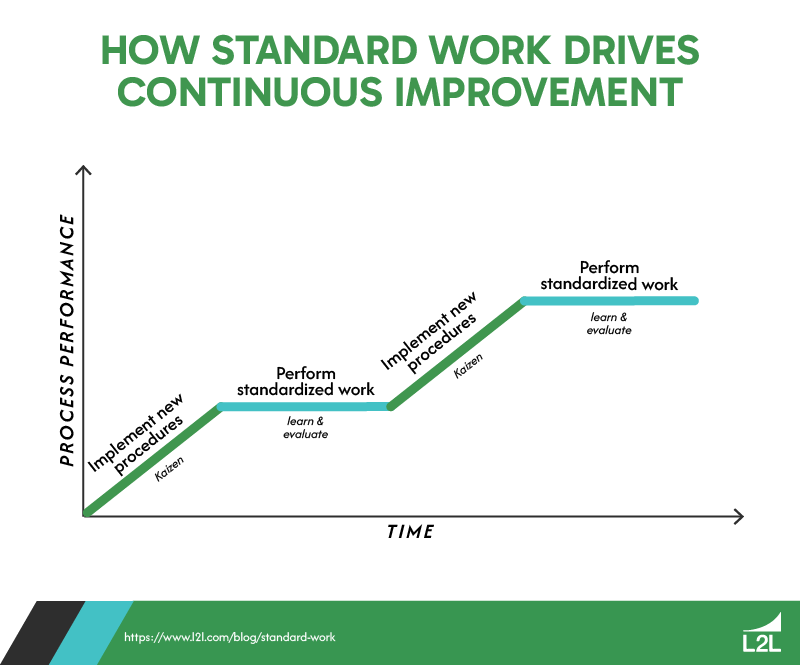
The concept of standard work originated from the Toyota Production System and lean principles. It’s considered a foundational part of Kaizen, or continuous improvement, due to its focus on quality control and its iterative nature.
Standard work takes on various forms within a manufacturing facility, but its main purpose is to enable workers to perform each task in the best way possible. It’s facilitated through various formats, including:
-
Daily process checks: These routine equipment inspections, such as machine inspections and material checks, ensure every aspect of the production process operates optimally and meets established standards of quality and efficiency.
-
Production checklists: Simpler and more task-specific than daily process checks, these step-by-step checklists are used during specific stages of the production process. They ensure that every required step is done correctly and in the right order and can include tasks like step-by-step instructions for equipment cleaning or changeovers.
-
Maintenance checklists: These checklists guide maintenance technicians through various preventive maintenance tasks (like parts replacement and machine testing) to ensure equipment stays in good working condition.
-
Operator asset care (OAC) checklists: OAC checklists enable operators to perform basic maintenance tasks, listing standard equipment care procedures like cleaning debris, lubrication, wear and tear inspection, filter replacements, and more.
-
Standard operating procedures (SOPs): SOPs are documented processes that outline each step needed to perform a task, such as machine startup or retooling, correctly and consistently, helping manufacturers achieve operational efficiency and compliance with industry standards.
-
Troubleshooting protocols: When a machine malfunctions, operators and technicians reference troubleshooting instructions that help them resolve issues safely, quickly, and effectively.
-
Training documents: Establishing standard work procedures begins with training documents, which should be frequently updated to reflect best practices and current mechanical and process knowledge. These documents can include operating instructions, company policies, and other role- and non-role-specific guidelines.
-
Safety protocols: Up-to-date safety instructions are typically part of manufacturing standard work and can include emergency response steps, material handling instructions, and PPE guidelines.
-
Quality checklists: Quality check protocols include a variety of defined procedures for inspecting finished products for defects. They include checklists that outline which features to inspect, inspection guidelines, and quality parameters.
When done right, standard work is infused into every production process. Documenting best practices and making them accessible to the right people at the right time is critical for maintaining high quality and efficiency standards.
Standard work implementation challenges and solutions
Standard work offers manufacturing facilities an array of benefits, including increases in productivity, efficiency, quality, safety, and profitability. However, implementing standard work often comes with several challenges that need to be managed proactively.
Here are some common challenges manufacturers encounter when introducing or optimizing standard work procedures — and how to address them.
Employee resistance
Resistance often occurs because employees may feel uncertain about new procedures or fear that these changes could make their jobs more difficult. A resistant workforce slows or even halts the adoption of new procedures.
To mitigate this, try to involve employees in the development of standard work procedures and openly discuss their benefits. Opening the floor for regular communication, demonstrating a commitment to employee welfare, and using connected technology to document and distribute information also help reduce resistance.
Inadequate training
If the training on new standard work procedures is rushed, lacks clarity, or neglects important details, workers may not fully grasp the new procedures.
Effective training programs should include hands-on practice, visual aids, and regular refresher sessions if needed. Ensuring that training is thorough and accessible through a digital platform will help employees feel more confident and competent in applying standard work practices.
Documentation and communication issues
Documentation that is unclear, overly complex, or inaccessible leads to inconsistencies in how procedures are performed. This can also occur if changes to procedures aren’t communicated effectively.
Standard work documents should be straightforward and use clear visuals where possible. Digitizing guidelines, making them accessible to the right people, and regularly updating and communicating procedural changes keep everyone on the same page.
Lack of flexibility
Overly rigid standard work procedures can prevent workers from creative problem-solving and exploring potential improvements. To maintain a culture of continuous improvement, allow employees to suggest changes.
This can be facilitated through programs like Kaizen, where workers are encouraged and rewarded for contributing ideas that enhance productivity or quality. Software solutions like connected workforce platforms, for instance, make it easy for workers to document issues and suggest improvements.
Monitoring and enforcement issues
Without a system to regularly check adherence to the procedures and to address deviations, compliance may wane over time. To stay in compliance with industry and government regulations, manufacturers should:
-
Perform regular audits
-
Centralize work instructions
-
Implement visual management systems
-
Establish feedback loops
-
Implement corrective action processes
By addressing these challenges effectively, a manufacturing facility can fully realize the benefits of implementing standard work, leading to improved consistency, efficiency, and quality in production. In turn, this creates a culture of “winning.”
Best practices for standardizing work in manufacturing
Optimizing standardized work requires careful planning and full visibility into shop floor performance metrics. Here are several steps for implementing standard work with a modern, workforce-centric approach.
1. Collect shop floor data
To successfully implement standard work procedures on the shop floor, you need to know where your current processes stand. Collect and analyze shop floor data through sensors, cloud computing methods, manufacturing software, and even worker input so you can accurately measure takt time.
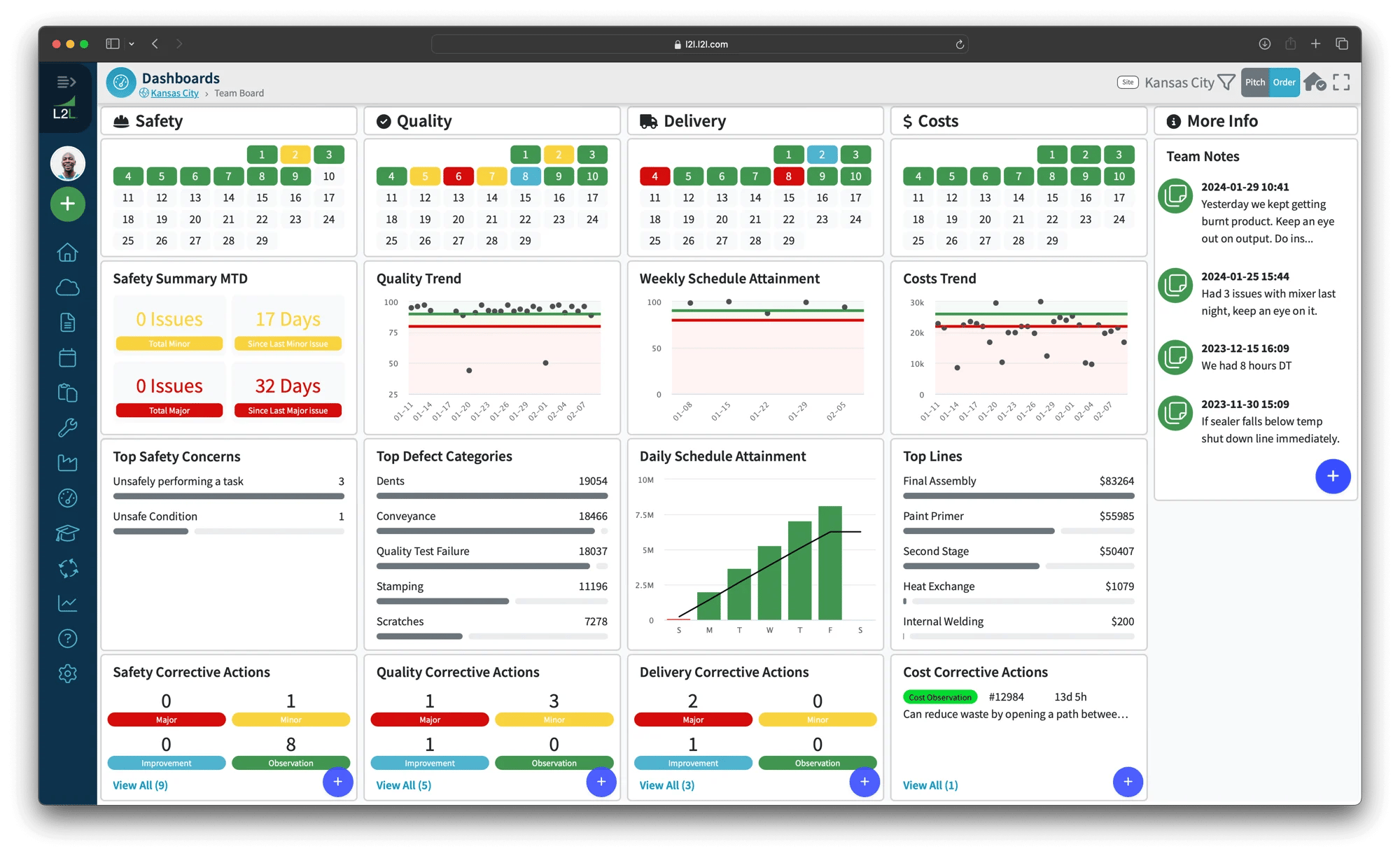
L2L TeamBoard visualizes real-time production, maintenance, and operational data.
Solutions like connected workforce platforms make machine and worker data collection seamless, with intuitive dashboards that display real-time line performance metrics.
2. Simplify feedback and adaptation
When implementing and refining standard work, worker feedback is critical for gauging the effectiveness of process adjustments. Make sure everyone affected by new procedures can easily provide and receive feedback.
Feedback loops are best facilitated through solutions like connected worker technology, which provides digital means for communication, note-taking, and updating task instructions. Letting workers report issues and suggest improvements in a centralized platform helps you quickly identify and adjust inefficient processes.
3. Document changes to standard work
Whenever you adjust a process, you must document the change and update affected workers immediately. It’s virtually impossible to keep everyone up-to-date on best practices without digital process documentation, especially if you’re running a large plant.
.png?width=3038&height=2136&name=image%20(3).png)
The L2L Connected Workforce Platform digitizes job-specific standard work instructions.
The most effective way to document and share process changes is by digitizing work instructions. This enables you to update and share guidelines with everyone on the shop floor, improving adherence to best practices.
4. Conduct ongoing training and development
Beyond initial training sessions, offer ongoing education and development opportunities to keep all employees up to speed with the latest standard work practices. This could include workshops, simulation-based training using augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) technology, and cross-training to help employees understand various roles and procedures.
Ongoing learning fosters a culture of continuous improvement and helps workers maintain high levels of competency and adherence to evolving standards.
5. Perform regular audits and reviews
Regularly audit and review the effectiveness of standard work procedures to ensure they remain relevant and effective. This involves periodically assessing the actual practices against the documented standards to identify discrepancies or areas for improvement. Audits help sustain the discipline required for standard work and reinforce the importance of adhering to established procedures.
Streamline standard work with the L2L Platform
Establishing and maintaining standard work is key to hitting production goals. Connected workforce platforms like L2L help manufacturers optimize performance and product quality by putting the right information, from maintenance checklists to SOPs, in front of workers at the right times.
-1.png?width=731&height=396&name=image%20(3)-1.png)
L2L's Operator Console displays a real-time view of machine and line performance data.
Our solution allows you to create, update, and distribute digital work instructions quickly and effectively. Skills management capabilities help you keep your workforce up-to-date on the latest safety and operational training while automatically alerting workers to deviations from standard procedures when necessary. Additionally, workers can access job-specific instructions, real-time insights, and communication channels from an intuitive, mobile-friendly platform.
To learn more about how L2L helps manufacturers across industries elevate standard work in their plants, book a personalized demo with one of our manufacturing technology experts!
But first, see how much money L2L can save your organization with our FREE ROI Tool. Our customers have seen upwards of 600% ROI over a few years — we’d love for you to be next!
Revisions
Original version: 23 April 2024
Written by: Evelyn DuJack
Reviewed by: Daan Assen
Please read our editorial process for more information
Related Posts
Subscribe to Our Blog
We won't spam you, we promise. Only informative stuff about manufacturing, that's all.




